Ovarian stimulation
Ovarian stimulation is the first phase of an IVF or artificial insemination treatment and it consists of inducing a multiple ovulation in the woman by administering hormonal medication
The objective of ovarian stimulation is for various follicles to develop simultaneously and to produce mature oocytes which can subsequently be extracted for fertilisation. Obtaining more than one oocyte per reproductive cycle allows us to optimise it as much as possible and to increase the pregnancy rate in assisted reproduction treatments, seeing as more than one embryo is available for the current cycle or for a later treatment with cryopreserved embryos.
The ovarian stimulation process

Before stimulating the ovaries, it is essential for us to perform a very precise diagnosis of the ovarian reserve, as this will allow us to find out what to expect in terms of the number of oocytes we will obtain and to assess the amount of medication we should administer, as this varies for each patient.
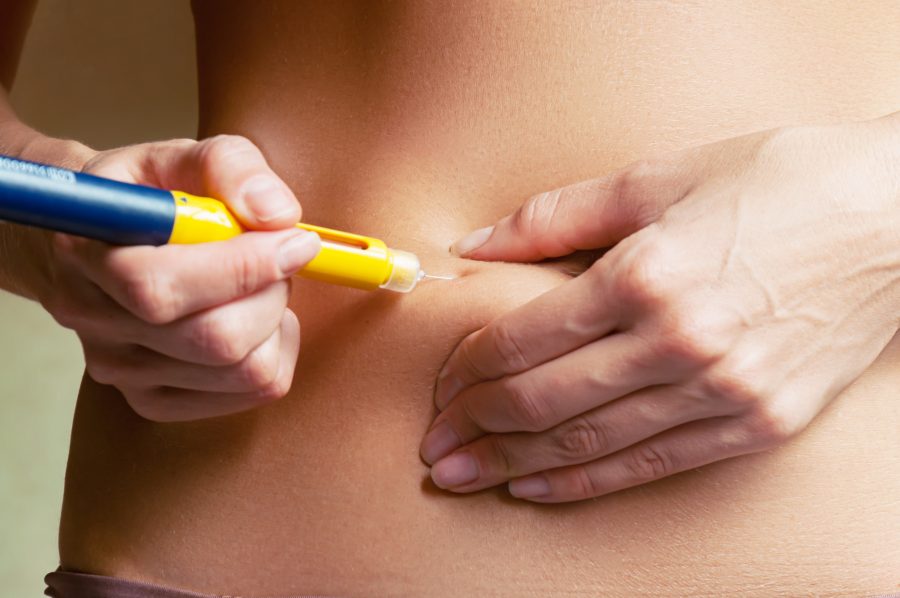
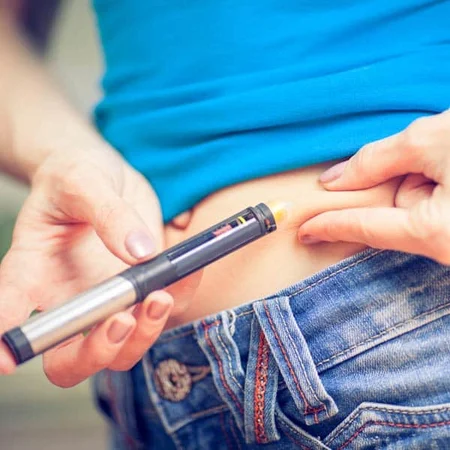
Ovarian stimulation is carried out via the administration of hormones called gonadotropins (FSH and HMG), which stimulate the growth of the ovarian follicles, and other medications which guarantee that the oocytes will remain within their follicles during the process.
This medication should be injected subcutaneously following the timeline that the specialist establishes for each patient, based on various factors (age, ovarian morphology, body mass, hormonal analysis, response in previous cycles, etc.).
Lastly, so that the eggs mature prior to extraction, we usually use a single dose of hCG hormone, knowing that ovulation will occur, i.e. the eggs will be pushed towards the tube, 34-36 hours after the administration of said hormone. Administering this hormone therefore allows the specialist to very precisely plan the surgical extraction of the eggs at the moment of optimum maturity.
How long does ovarian stimulation take?
Usually, ovarian stimulation is carried out for between 8 and 14 days and it normally starts on the second or third day of menstruation with the administration of the appropriate hormonal medication.
Regular ultrasound checks are performed throughout the process along with blood tests to ensure that follicular growth and maturity are adequate and to determine the best day to extract the eggs.