Reproducción asistida
Sperm survival test
The sperm survival test or sperm capacitation test is, along with the seminogram, one of the routine diagnostic tests that measures male infertility.
The sperm survival test evaluates the seminal parameters needed to achieve egg fertilisation naturally or using assisted reproduction techniques. The following aspects are analysed:
- The motility of the spermatozoa after they have gone through the capacitation process.
- The sperm survival rate, after 24 hours in a CO2 atmosphere.
- Additionally, we evaluate the presence or absence of bacterial contamination in the capacitated sample.
Sperm capacitation
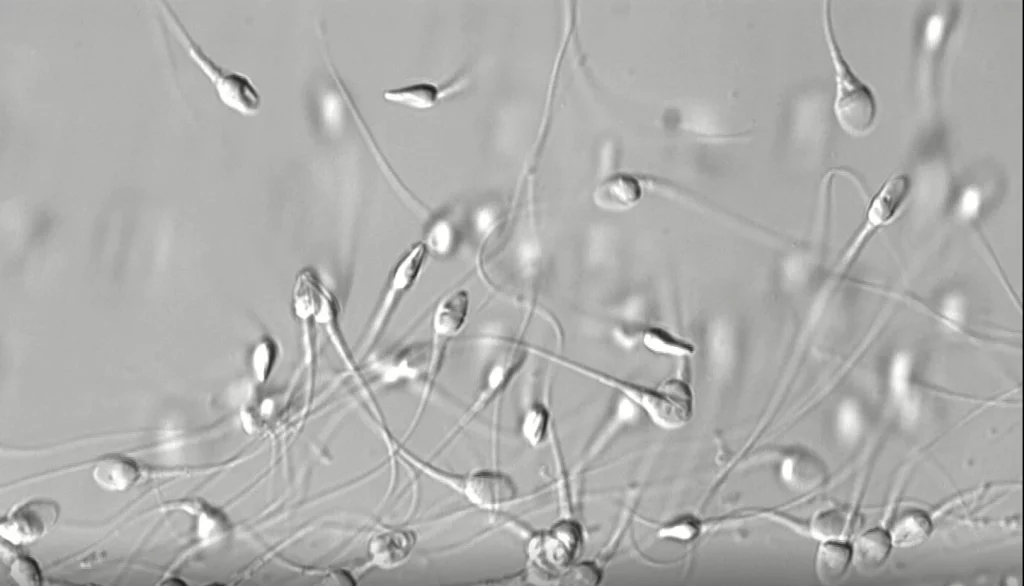
Sperm capacitation is defined as the set of physiological changes that a spermatozoon must undergo in order to gain the ability to fertilise an egg.
Spermatozoa acquire this fertilisation capacity in the female reproductive system, during their migration through the cervical mucus. Sperm capacitation can also be achieved without natural means, i.e. ‘in vitro’ in the lab using two different techniques: swim-up and density gradients.
These techniques separate the spermatozoa from the seminal plasma, thus obtaining those that can move the best. The result of using these techniques to achieve capacitation is called the MSC (Motile Sperm Count) and its unit of measurement is the number of spermatozoa that move in a straight line
Obtaining the semen sample for the sperm survival test
To guarantee that the diagnostic is as reliable as possible, the semen sample must be obtained following the guidelines below:
- Maintain 2 to 4 days of sexual abstinence. The limits are no less than 2 days and no more than 4 days of abstinence. If there is any less abstinence, there would be anomalous sperm concentrations and if there is more, then we would see anomalous sperm motility parameters.
- Gather the sample in a sterile container: Ginefiv will provide one but they are also available for purchase in any pharmacy.
- The way that the sample is obtained must be masturbation, and neither coitus interruptus nor the use of commercially available condoms is valid.
- Maintain maximum hygiene conditions for the sample collection (wash hands beforehand, etc.).
- Ensure that the sample is complete: if part of it is not captured in the container, the sample is not valid.
If the sample is collected at home:
- Once the sample has been obtained, you must ensure that the container is fully closed and that its temperature does not drop (it must be kept at body temperature [36°-37°], avoiding brusque temperature changes) and therefore we recommend carrying it in an inner pocket.
- If you have had a fever in the 7-10 days prior to the collection of the semen sample or if you have taken any antibiotics, you must contact the lab to postpone the appointment
Results of the sperm survival test
Once the sperm count is complete and the results of the seminogram have been obtained, an assisted reproduction specialist will advise you depending on the sterility issue we found (the following recommendations are for information purposes only):
- Usually, if the post-capacitation MSC is over 5 million progressive motile spermatozoa, we recommend artificial insemination.
- If there are over 1 million but below 5 million progressive motile spermatozoa post capacitation, we recommend conventional IVF.
- And if there are less than 1 million progressive motile spermatozoa post capacitation, we recommend ICSI (sperm microinjection).